A Natural-language-based Visual Query Approach of Uncertain Human Trajectories
Zhaosong Huang, Ye Zhao, Wei Chen, Shengjie Gao, Kejie Yu, Weixia Xu, Mingjie Tang, Minfeng Zhu, and Mingliang Xu.
IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics (VIS 2019 VAST TVCG track).
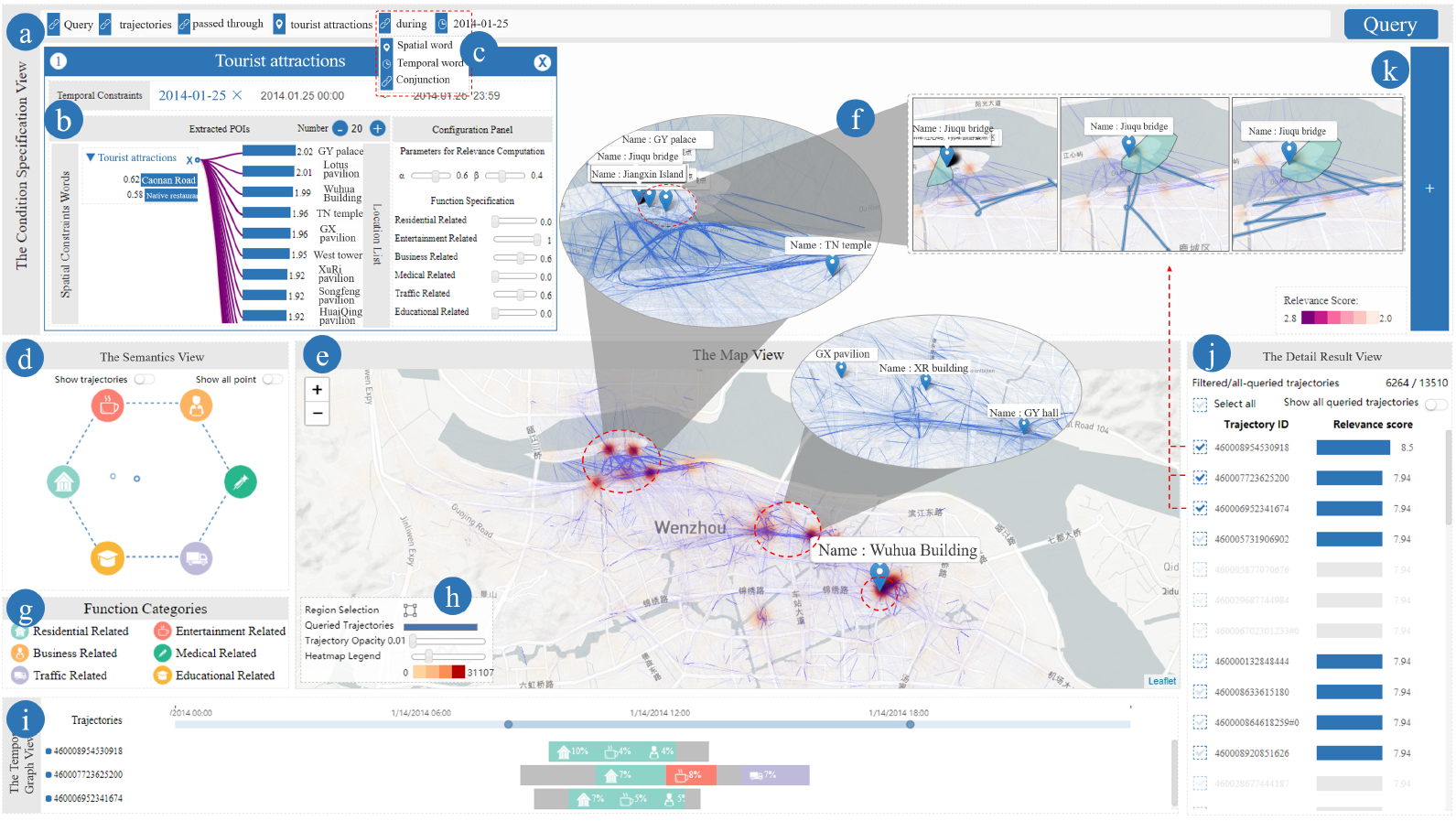
Visual querying is essential for interactively exploring massive trajectory data. However, the data uncertainty imposes profound challenges to fulfill advanced analytics requirements. On the one hand, many underlying data does not contain accurate geographic coordinates, e.g., positions of a mobile phone only refer to the regions (i.e., mobile cell stations) in which it resides, instead of accurate GPS coordinates. On the other hand, domain experts and general users prefer a natural way, such as using a natural language sentence, to access and analyze massive movement data. In this paper, we propose a visual analytics approach that can extract spatial-temporal constraints from a textual sentence and support an effective query method over uncertain mobile trajectory data. It is built up on encoding massive, spatially uncertain trajectories by the semantic information of the POIs and regions covered by them, and then storing the trajectory documents in text database with an effective indexing scheme. The visual interface facilitates query condition specification, situation-aware visualization, and semantic exploration of large trajectory data. Usage scenarios on real-world human mobility datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
location2vec: a situation-aware representation for visual exploration of urban locations.
Minfeng Zhu, Wei Chen, Jiazhi Xia, Yuxin Ma, Yankong Zhang, Yuetong Luo, Zhaosong Huang, Liangjun Liu.
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (TITS 2019).
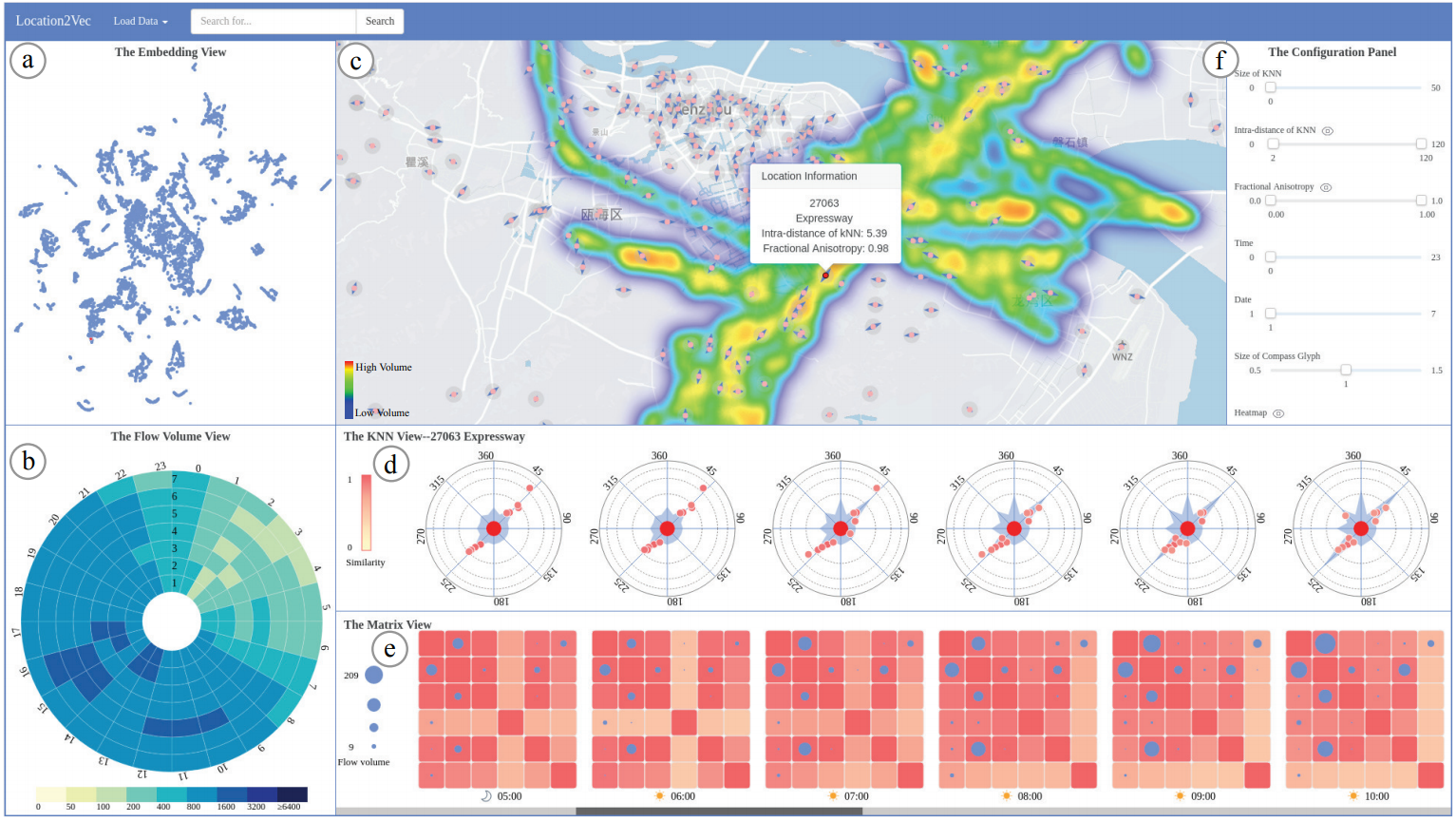
Understanding the relationship between urban locations is an essential task in urban planning and transportation management. Whereas prior works have focused on studying urban locations by aggregating location-based properties, our scheme preserves the mutual influence between urban locations and mobility behavior, and thereby enables situation-aware exploration of urban regions. By leveraging word embedding techniques, we encode urban locations with a vectorized representation while retaining situational awareness. Specifically, we design a spatial embedding algorithm that is precomputed by incorporating the interactions between urban locations and moving objects. To explore our proposed technique, we have designed and implemented a web-based visual exploration system that supports the comprehensive analysis of human mobility, location functionality, and traffic assessment by leveraging the proposed visual representation. Case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Exploring the Sensitivity of Choropleths under Attribute Uncertainty.
Zhaosong Huang, Yafeng Lu, Elizabeth Mack, Wei Chen, and Ross Maciejewski.
IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics (TVCG 2019).
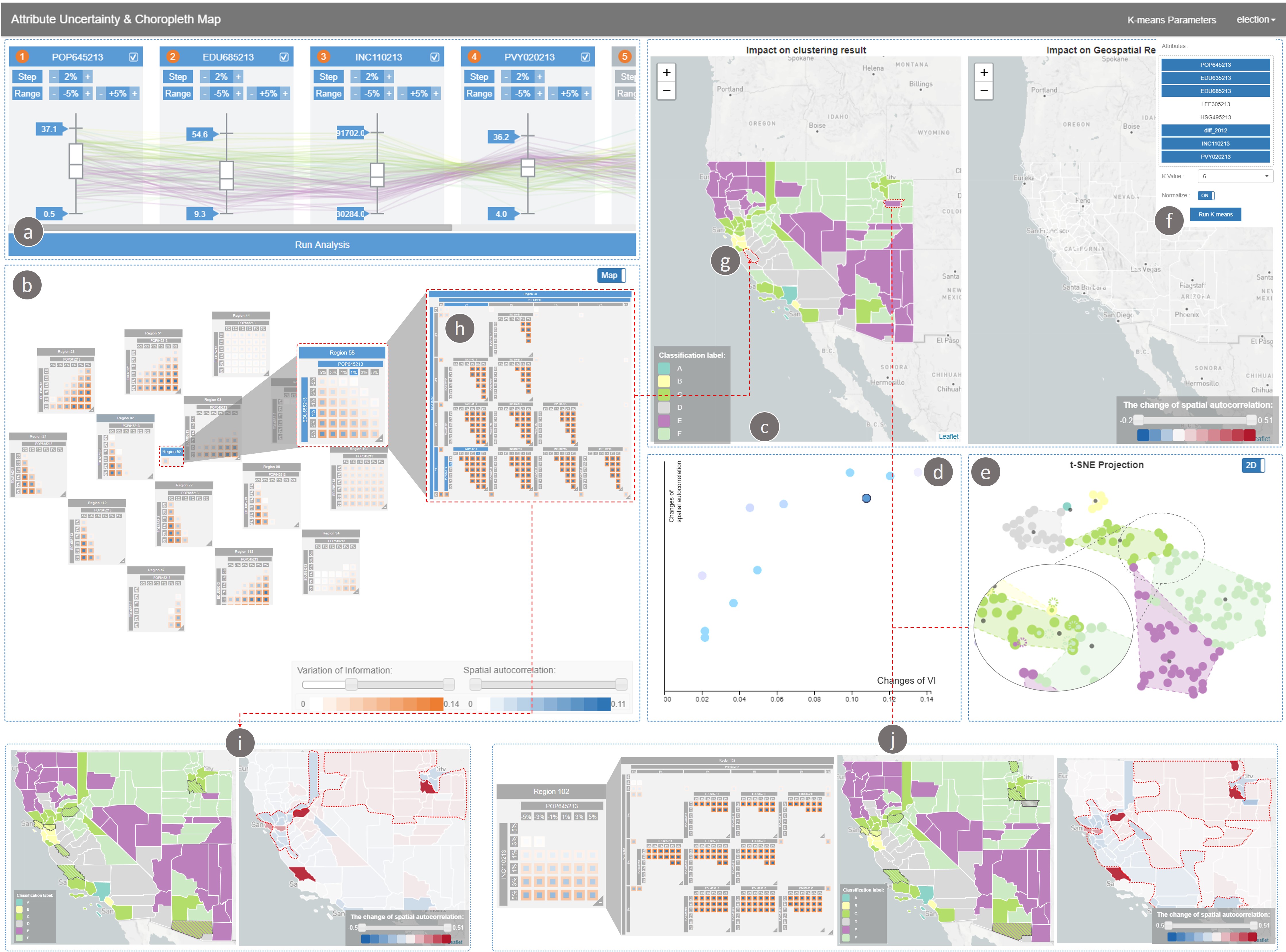
The choropleth map is an essential tool for spatial data analysis. However, the underlying attribute values of a spatial unit greatly influence the statistical analyses and map classification procedures when generating a choropleth map. If the attribute values incorporate a range of uncertainty, a critical task is determining how much the uncertainty impacts both the map visualization and the statistical analysis. In this paper, we present a visual analytics system that enhances our understanding of the impact of attribute uncertainty on data visualization and statistical analyses of these data. Our system consists of a parallel coordinates-based uncertainty specification view, an impact river and impact matrix visualization for region-based and simulation-based analysis, and a dual-choropleth map and t-SNE plot for visualizing the changes in classification and spatial autocorrelation over the range of uncertainty in the attribute values. We demonstrate our system through three use cases illustrating the impact of attribute uncertainty in geographic analysis.
Vaud: A visual analysis approach for exploring spatio-temporal urban data.
Chen, Wei, Zhaosong Huang, Feiran Wu, Minfeng Zhu, Huihua Guan, and Ross Maciejewski.
IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, 24(9), 2636-2648 (TVCG 2018).
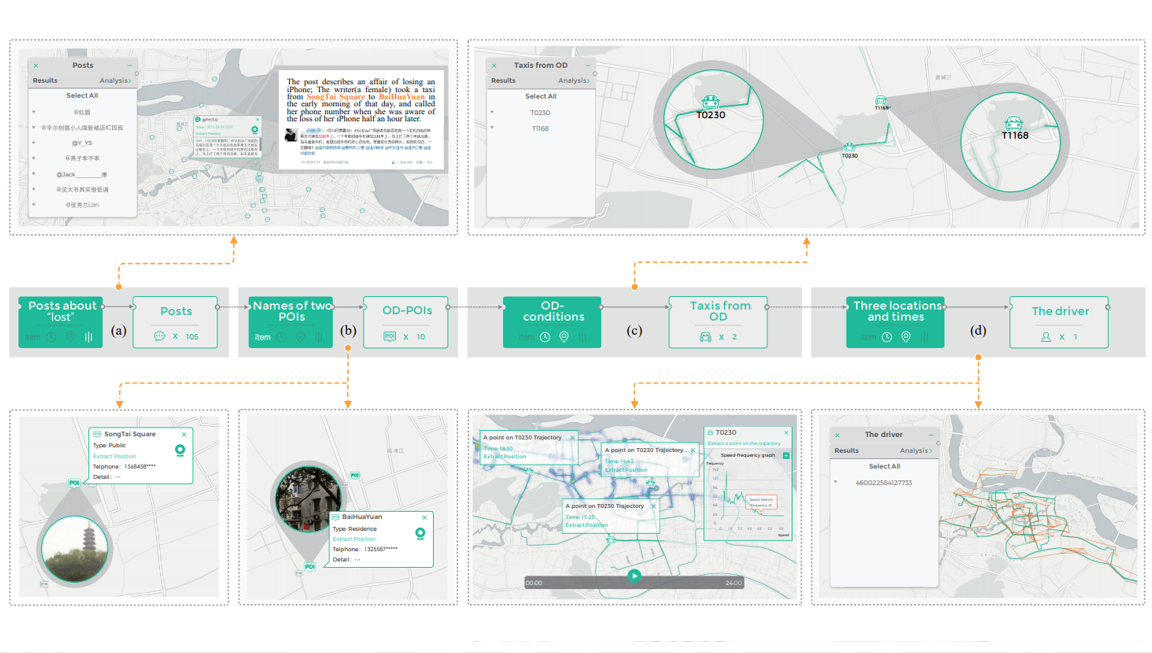
Urban data is massive, heterogeneous, and spatio-temporal, posing a substantial challenge for visualization and analysis. In this paper, we design and implement a novel visual analytics approach, Visual Analyzer for Urban Data (VAUD), that supports the visualization, querying, and exploration of urban data. Our approach allows for cross-domain correlation from multiple data sources by leveraging spatial-temporal and social inter-connectedness features. Through our approach, the analyst is able to select, filter, aggregate across multiple data sources and extract information that would be hidden to a single data subset. To illustrate the effectiveness of our approach, we provide case studies on a real urban dataset that contains the cyber-, physical-, and socialinformation of 14 million citizens over 22 days.
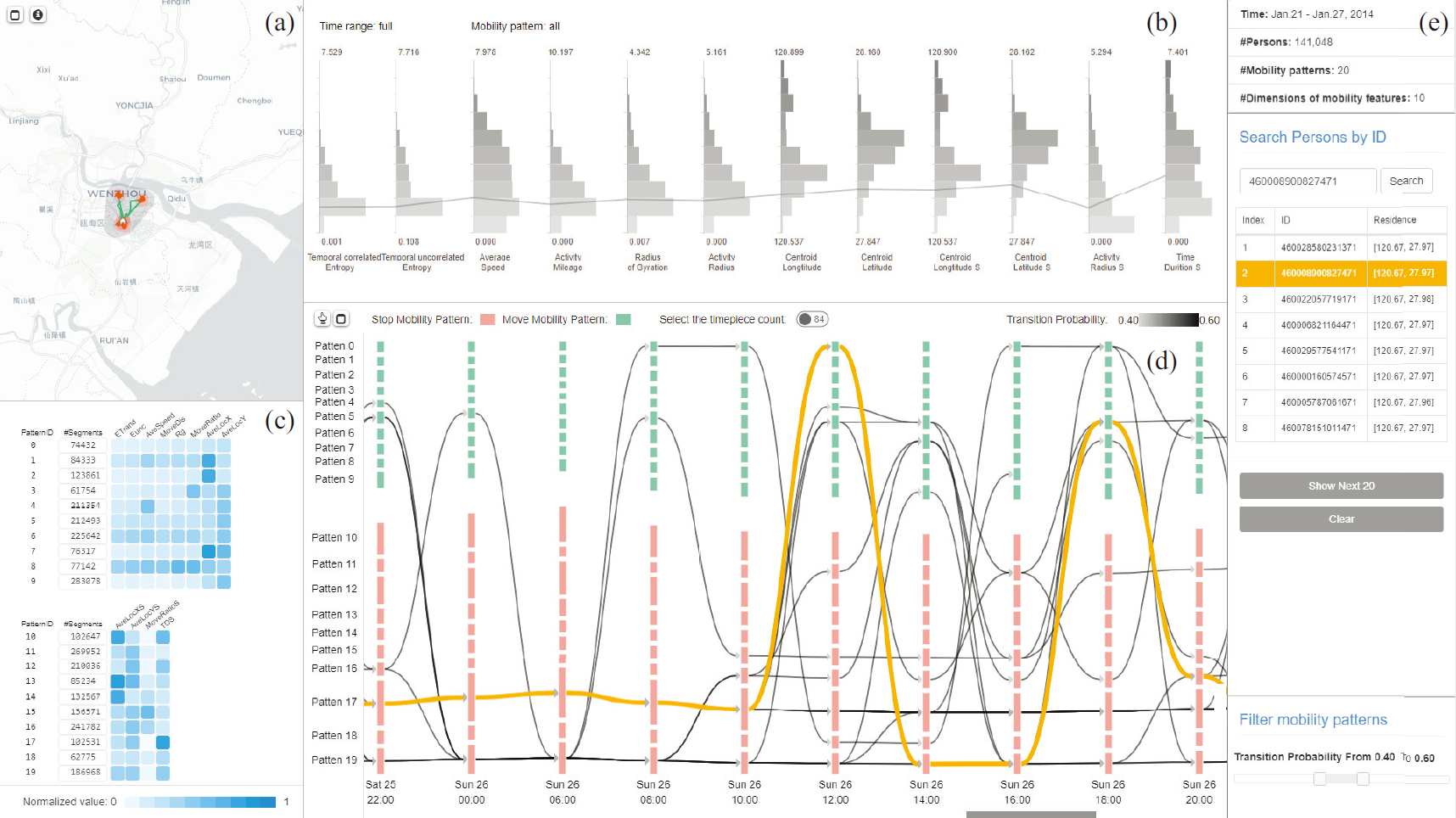
Structuring Mobility Transition With an Adaptive Graph Representation.
Gu, Tianlong, Minfeng Zhu, Wei Chen, Zhaosong Huang, Ross Maciejewski, and Liang Chang.
IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, (99), pp.1-12.
Modeling human mobility is a critical task in fields such as urban planning, ecology, and epidemiology. Given the current use of mobile phones, there is an abundance of data that can be used to create models of high reliability. Existing techniques can reveal the macro-patterns of crowd movement or analyze the trajectory of a person; however, they typically focus on geographical characteristics. This paper presents a graph-based approach for structuring crowd mobility transition over multiple granularities in the context of social behavior. The key to our approach is an adaptive data representation, the adaptive mobility transition graph, that is globally generated from citywide human mobility data by defining the temporal trends of human mobility and the interleaved transitions between different mobility patterns. We describe the design, creation and manipulation of the adaptive mobility transition graph and introduce a visual analysis system that supports the multi-faceted exploration of citywide human mobility patterns.
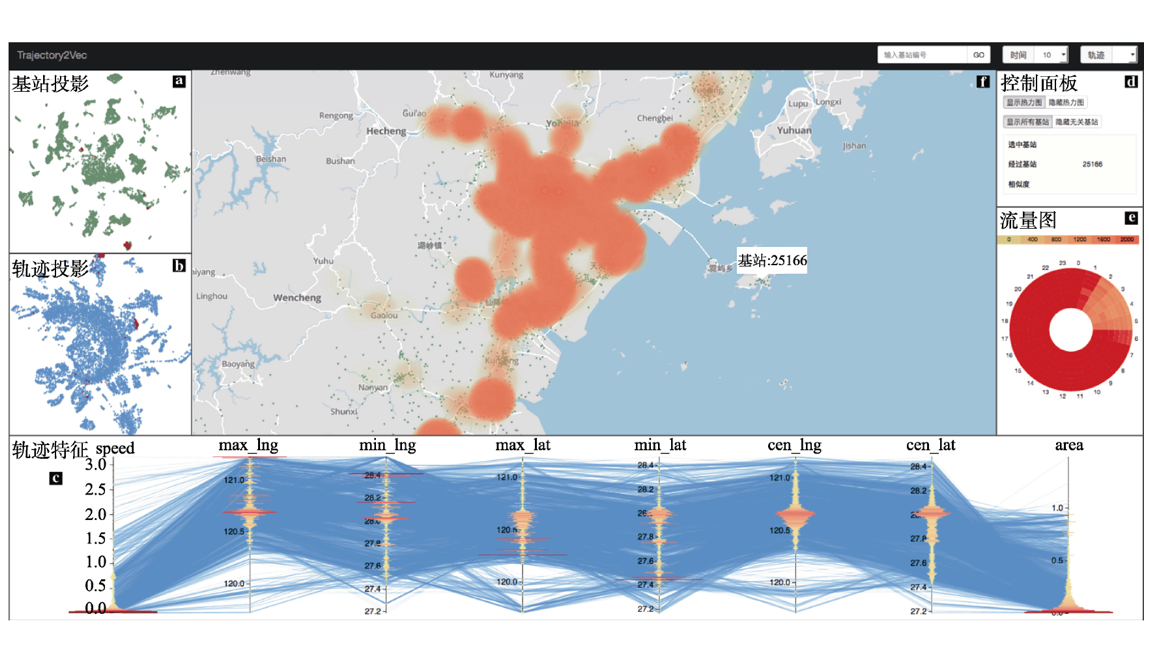
一个基于基站轨迹数据的城市移动模式可视分析系统.
李致昊, 朱闽峰, 黄兆嵩, 丁铁成, 罗月童, 葛嘉恒, & 陈为.
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报 30, no. 1 (2018): 68-78.
随着移动通信技术的发展, 手机基站轨迹数据在分析人类移动规律方面的优势日趋显著. 由于人群移动模式与其社会行为息息相关, 该模式能够直接反映各地理区块在不同时间段所具备的社会功能. 根据词嵌入模型, 首先将基站的时空信息映射为向量, 通过计算基站间的高层语义的相似规律来分析地理区域的功能性信息; 再将带有时空变化信息的手机用户移动轨迹映射至向量空间, 使基站地理坐标与轨迹相结合, 从而获取更加丰富的语义信息.在交互方面, 设计了一个可视化分析系统 Trajectory2Vec 来探索城市区域功能和用户行为的关系, 案例分析证明了该系统可以有效地帮助用户分析移动人群与城市区域间关系的动态变化规律.